What is DevOps and Its Stages ?
The key to understanding what is DevOps lies in the intention of DevOps, that is to create superior-quality software, more quickly and with more reliability while causing greater communication and collaboration between teams. By teams, we refer to these two: Development team & IT Operations team.
In-fact, it is not the collaboration between these two teams which help deliver better software, but the oneness between ‘Dev’ & ‘Ops’ teams which results in improved software, delivered at a greater velocity. And let’s not forget the role played by DevOps tools for achieving automation. They rather sit at the foundation and help support the entire DevOps structure.
The feeling of ‘oneness’, is caused by the bridging of skill-sets & practices between Developers and Operation Engineers, and the implementation of automation (DevOps) tools. Leading organizations across the world have adopted DevOps methodologies to overhaul their performance, security and team dynamics. With more and more companies jumping on to the DevOps bandwagon, it has emerged as ahot skill to master in 2016.
In this blog, let us find out what is DevOps and why is it such a big deal! We will do this by first tracing the evolution of software development methodologies leading to DevOps, then exploring what is DevOps and its life cycle, and finish up by evaluating how top companies such as Facebook are using DevOps to their benefit.
Evolution of Software Development
DevOps evolved from existing software development strategies/ methodologies over the years in response to business needs. Let us briefly look at how these models evolved and in which scenarios they would work best.
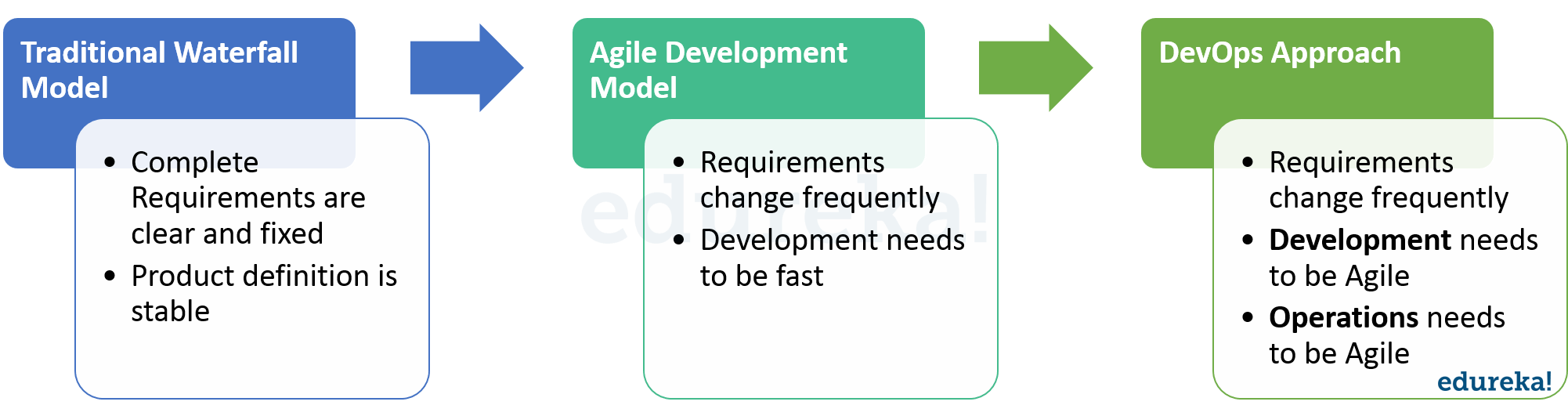
The slow and cumbersome Waterfall model evolved into Agile which saw development teams working on the software in short sprints lasting not more than two weeks. Having such a short release cycle helped the development team work on client feedback and incorporate it along with bug fixes in the next release. While this Agile SCRUM approach brought agility to development, it was lost on Operations which did not come up to speed with Agile practices. Lack of collaboration between Developers and Operations Engineers still slowed down the development process and releases. DevOps methodology was born out of this need for better collaboration and faster delivery. DevOps enables continuous software delivery with less complex problems to fix and faster resolution of problems.
Now that we have understood the evolution of DevOps, let us look at what is DevOps in detail.
What is DevOps?
DevOps is a software development approach which involves Continuous Development, Continuous Testing, Continuous Integration, Continuous Deployment and Continuous Monitoring of the software throughout its development life cycle. These activities are possible only in DevOps, not Agile or waterfall, and this is why Facebook and other top companies have chosen DevOps as the way forward for their business goals. DevOps is the preferred approach to develop high quality software in shorter development cycles which results in greater customer satisfaction. Check out the below video on What is DevOps before you go ahead.
Your understanding of what is DevOps is incomplete without learning about its life cycle. Let us now look at the DevOps life cycle and explore how they are related to the software development stages depicted in the diagram below.
Your understanding of what is DevOps is incomplete without learning about its life cycle. Let us now look at the DevOps life cycle and explore how they are related to the software development stages depicted in the diagram below.
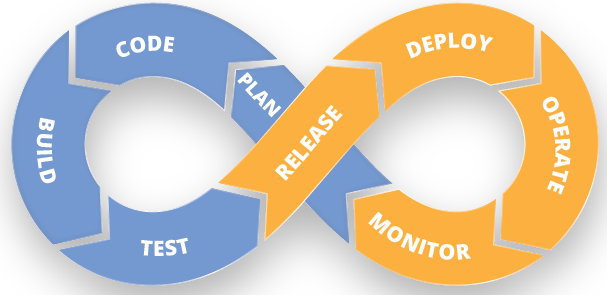
Continuous Development:
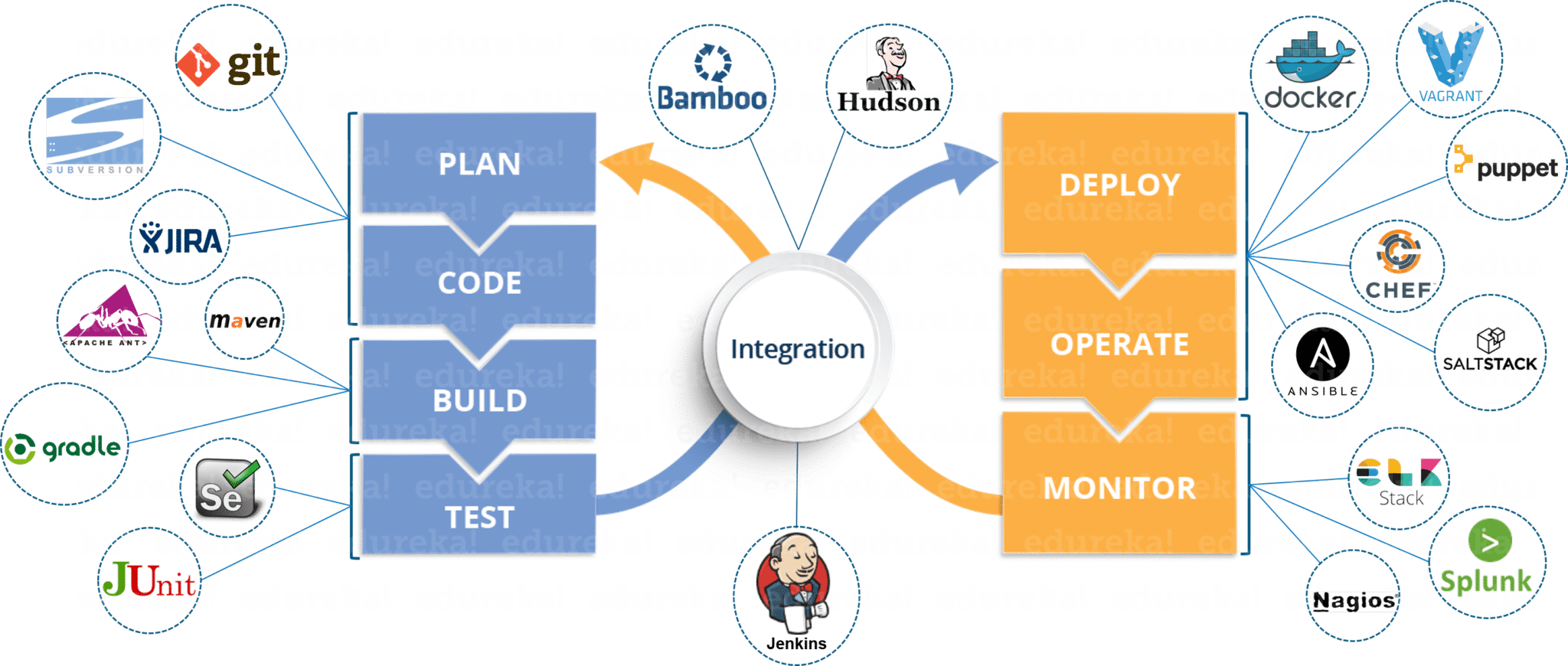
This is the stage in the DevOps life cycle where the Software is developed continuously. Unlike the Waterfall model, the software deliverables are broken down into multiple sprints of short development cycles, developed and then delivered in a very short time. This stage involves the Coding and Building phases and makes use of tools such as Git and SVN for maintaining the different versions of the code, and tools like Ant, Maven, Gradle for building/ packaging the code into an executable file that can be forwarded to the QAs for testing.
Continuous Testing:
This is the stage where the developed software is continuously tested for bugs. For Continuous testing, automation testing tools like Selenium, TestNG, JUnit, etc are used. These tools allow the QAs to test multiple code-bases thoroughly in parallel to ensure that there are no flaws in the functionality. In this phase, use of Docker containers for simulating ‘test environment’ on the fly, is also a preferred choice. Once the code is tested, it is continuously integrated with the existing code.
Continuous Integration:
This is the stage where the code supporting new functionality is integrated with the existing code. Since there is continuous development of software, the updated code needs to be integrated continuously as well as smoothly with the systems to reflect changes to the end users. The changed code, should also ensure that there are no errors in the runtime environment, allowing us to test the changes and check how it reacts with other changes.
Jenkins is a very popular tool used for Continuous Integration. Using Jenkins, one can pull the latest code revision from GIT repository and produce a build which can finally be deployed to test or production server. It can be set to trigger a new build automatically as soon as there is a change in the GIT repository or can be triggered manually on click of a button.
Continuous Deployment:
It is the stage where the code is deployed to the production environment. Here we ensure that the code is correctly deployed on all the servers. If there is any addition of functionality or a new feature is introduced then one should be ready to welcome greater website traffic. So it is also the responsibility of the SysAdmin to scale up the servers to host more users.
Since the new code is deployed on a continuous basis, configuration management tools play an important role for executing tasks quickly and frequently. Puppet, Chef, SaltStack and Ansible are some popular tools that are used in this stage.
Containerization tools also play an important role in the deployment stage. Docker and Vagrant are the popular tools which help produce consistency across Development, Test, Staging and Production environments. Besides this, they also help in scaling-up and scaling-down of instances easily.
Continuous Monitoring:
This is a very crucial stage in the DevOps life cycle which is aimed at improving the quality of the software by monitoring its performance. This practice involves the participation of the Operations team who will monitor the user activity for bugs / any improper behavior of the system. This can also be achieved by making use of dedicated monitoring tools which will continuously monitor the application performance and highlight issues.
Some popular tools used are Splunk, ELK Stack, Nagios, NewRelic and Sensu. These tools help you monitor the application and the servers closely to check the health of the system proactively. They can also improve productivity and increase the reliability of the systems, reducing IT support costs. Any major issues found could be reported to the development team so that it can be fixed in the continuous development phase.
These DevOps stages are carried out on loop continuously until the desired product quality is achieved. The diagram given below will show you which tools can be used in which stage of the DevOps life cycle.
Comments
Post a Comment